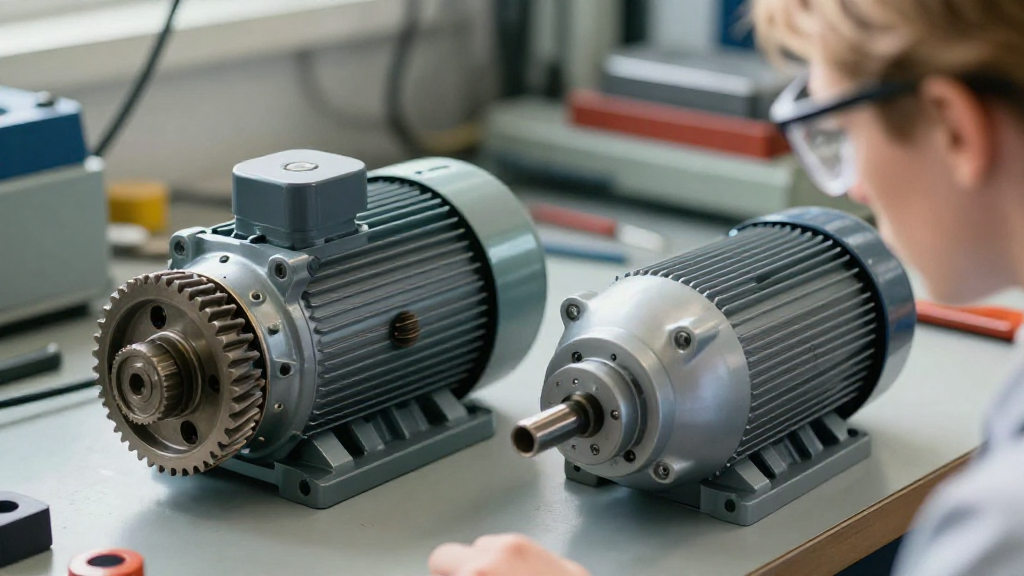
When it comes to selecting a motor for your application, you may find yourself asking: geared vs direct drive motors—which is the best choice?
In this article, we will delve into the differences between geared and direct drive motors, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and the applications where each excels. By the end, you should have a clearer understanding to make an informed decision.
What Are Geared Motors?
Geared motors utilize a gearbox to increase torque output while reducing the speed of the motor. This setup transforms the motor’s high-speed, low-torque output into a more usable form for various applications.
Key Features of Geared Motors:
- High Torque Output: Ideal for applications requiring significant force.
- Speed Reduction: Suitable for slowing down rotational speed to match application requirements.
- Compact Size: While they can be bulkier than direct drive motors, they offer a compact solution for high-torque applications.
Common Applications of Geared Motors:
- Conveyors
- Robotics
- Automotive
- Industrial machinery
What Are Direct Drive Motors?
Direct drive motors differ significantly from geared motors in that they do not use a gearbox. Instead, these motors achieve precise control without the need for mechanical gearing.
Key Features of Direct Drive Motors:
- No Gearing Loss: Direct drive motors maintain high efficiency due to the absence of a gearbox.
- Precision Control: They provide excellent speed and positioning control.
- Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts, they require less maintenance over time.
Common Applications of Direct Drive Motors:
- CNC machines
- Electric vehicles
- Medical devices
- Aerospace technology
What Are the Major Differences Between Geared and Direct Drive Motors?
Now let’s explore the various factors to consider when comparing geared vs direct drive motors.
1. Torque and Speed
- Geared Motors: Offer high torque at low speeds.
- Direct Drive Motors: Provide high speed with lower torque.
The choice here largely depends on the specific requirements of your application. For instance, a conveyor belt may benefit from the high torque of a geared motor, while a CNC machine could leverage the precision of a direct drive motor.
2. Efficiency
- Geared Motors: Typically less efficient due to friction in the gears.
- Direct Drive Motors: Generally more efficient, leading to lower energy costs.
If energy efficiency is a priority, direct drive motors may be the better option in the geared vs direct drive motors debate.
3. Size and Space Considerations
- Geared Motors: Can take up more space due to the gearbox.
- Direct Drive Motors: Often more compact, allowing for easier integration in tight spaces.
In applications where space is at a premium, direct drive motors may offer a significant advantage.
4. Control and Precision
- Geared Motors: Offer good control but may incur lag due to gear movement.
- Direct Drive Motors: Provide superior precision and responsiveness.
If your application requires high precision, such as robotic arms or CNC machining, direct drive motors will prove beneficial.
What Are the Advantages of Geared Motors?
Despite the advancements of direct drive technology, geared motors still possess distinct advantages:
Advantages of Geared Motors:
- Cost-Effective: Typically more affordable than direct drive motors.
- High Starting Torque: Great for applications needing substantial force from a standstill.
- Wide Range of Ratios: Allowing users to customize output to fit their needs.
In certain applications, these benefits make geared motors the preferred choice.
What Are the Advantages of Direct Drive Motors?
Understanding the benefits of direct drive motors can help in deciding between geared vs direct drive motors for specific applications:
Advantages of Direct Drive Motors:
- High Efficiency: Minimizing energy loss means lower operational costs.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Fewer moving parts lead to decreased maintenance needs.
- Smooth Operation: Ideal for applications requiring precise movements.
In scenarios where efficiency and precision are of utmost importance, direct drive motors shine.
How to Choose Between Geared and Direct Drive Motors?
When considering geared vs direct drive motors, you should evaluate the following criteria:
1. Application Requirements:
- What is the nature of your application?
- Do you need high torque, or is precision more crucial?
2. Cost Considerations:
- What is your budget?
- Cost may be a decisive factor depending on your resources.
3. Space Constraints:
- Do you have room for a larger gearbox, or is a compact solution necessary?
4. Long-Term Maintenance:
- How often are you willing to maintain the motor?
- Direct drive motors require less maintenance than geared motors.
Conclusion: Which is Right for Your Needs?
The choice between geared vs direct drive motors really depends on the specifics of your application.
- If you prioritize high torque and lower initial costs, geared motors may be your best option.
- However, if you are looking for efficiency, precision, and reduced maintenance, direct drive motors stand out as the superior choice.
Ultimately, both types of motors have their unique advantages, and understanding your particular needs is crucial for making the right decision.
Remember to weigh the pros and cons of each type within the context of your project requirements.
With this knowledge, you’ll be equipped to choose the motor type that best suits your application needs—ensuring your projects are successful, efficient, and cost-effective.